
Rear door heat exchangers (RDHx) are a type of cooling solution used in data centers that work by removing heat from the exhaust air of IT equipment using a heat exchanger installed on the back of the server rack. The cooled air is then recirculated into the data center, reducing the need for traditional computer room air conditioning (CRAC) units.
RDHx can be an efficient way of air cooling in data centers under certain circumstances, but it may not always be the most efficient solution. Here are some factors to consider:
Heat Load: RDHx is most efficient when the heat load is high and the density of IT equipment is high. In such scenarios, the RDHx can remove heat directly from the IT equipment, providing efficient cooling.
Climate: RDHx may not be the most efficient cooling solution in hot and humid climates, where the ambient air temperature and humidity are high. In such conditions, the RDHx may struggle to remove enough heat from the exhaust air, and additional cooling may be required.
Server Design: RDHx may not be compatible with all server designs, particularly those not rear-facing. In such cases, alternative cooling solutions such as in-row cooling or liquid cooling may be more efficient.
Maintenance: RDHx requires regular maintenance to ensure they are functioning correctly. The heat exchanger and filters need to be cleaned regularly to prevent a build-up of dust and other contaminants that can reduce their efficiency.
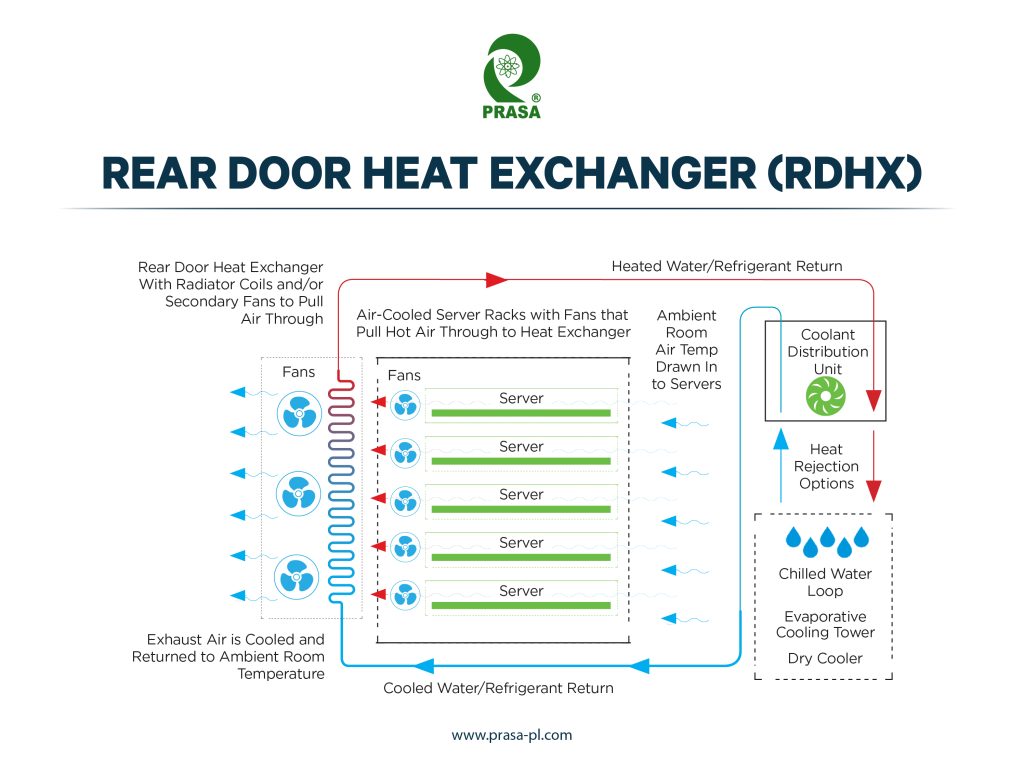 In summary, RDHx can be an efficient way of air cooling in data centers when the heat load is high and the density of IT equipment is high. However, their efficiency can be affected by factors such as climate, server design, and maintenance requirements. Ultimately, the most efficient cooling solution will depend on the specific needs and constraints of the data center.
In summary, RDHx can be an efficient way of air cooling in data centers when the heat load is high and the density of IT equipment is high. However, their efficiency can be affected by factors such as climate, server design, and maintenance requirements. Ultimately, the most efficient cooling solution will depend on the specific needs and constraints of the data center.

