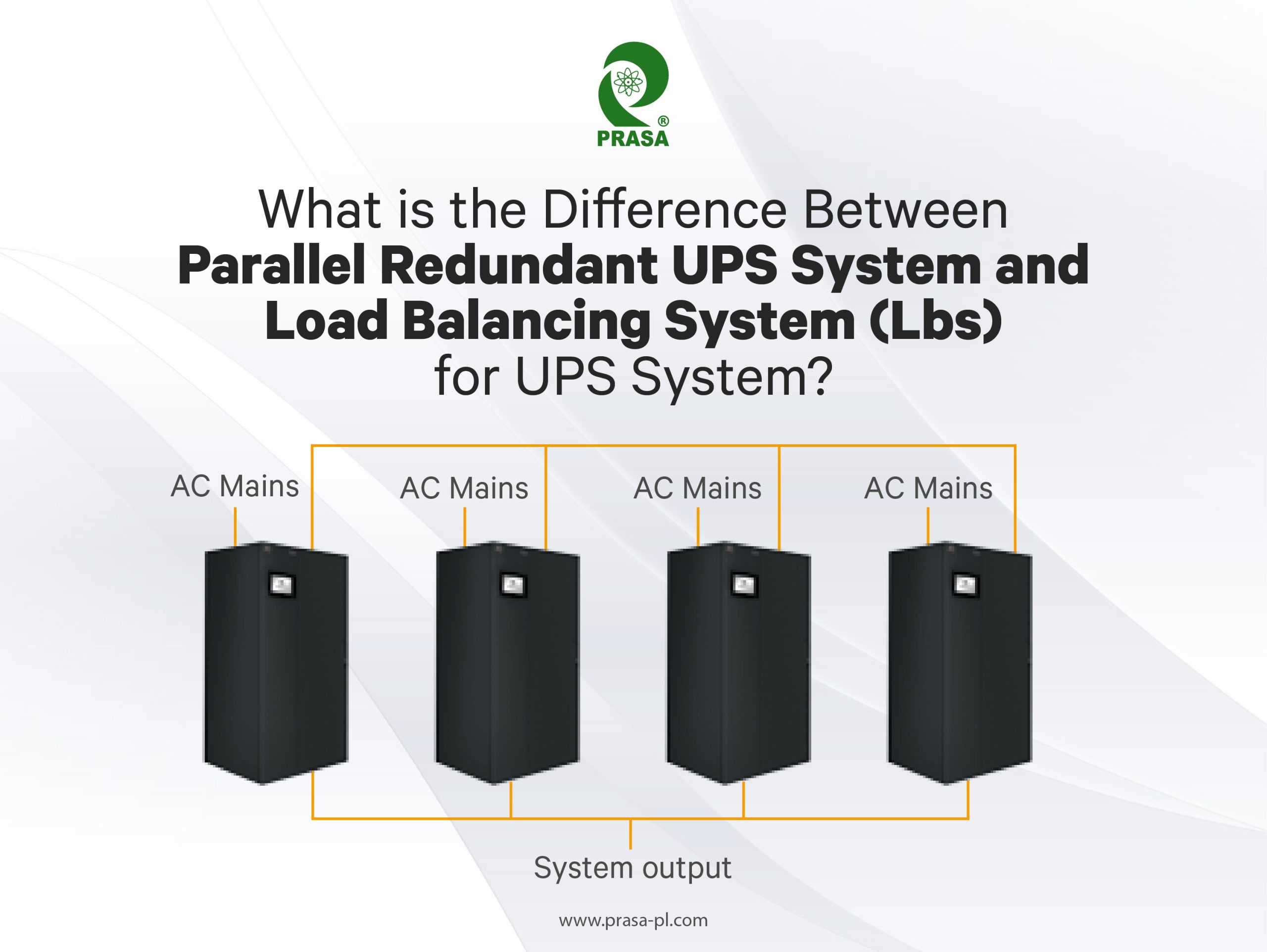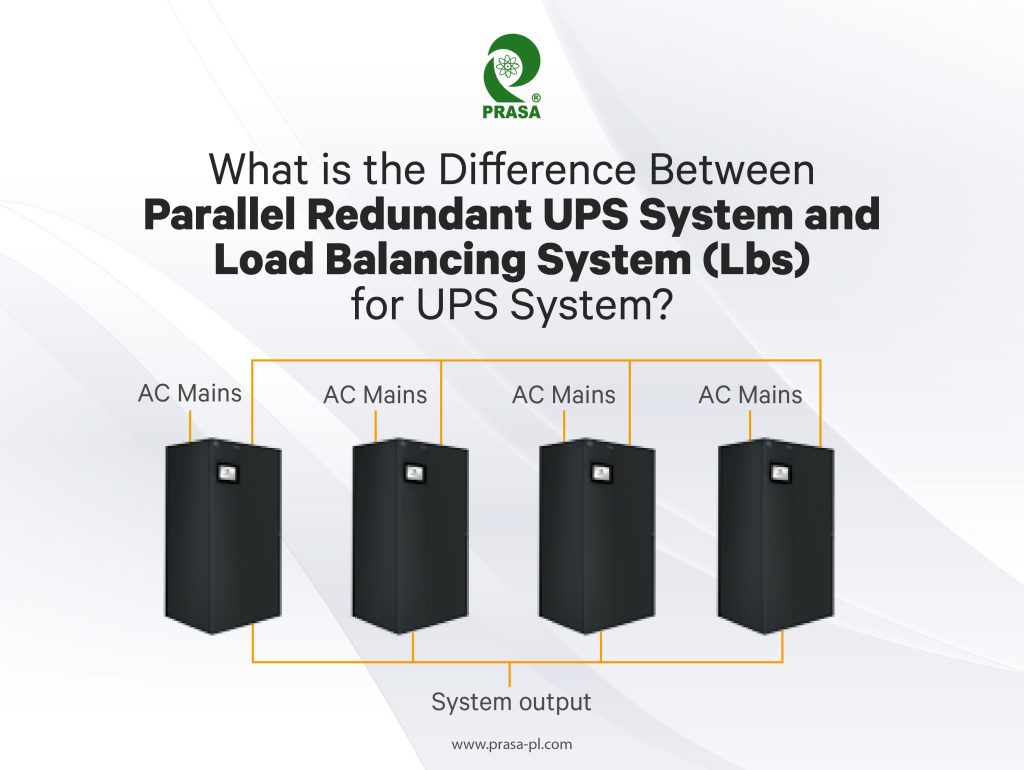
Parallel redundant UPS systems and load balancing systems (LBS) are two different approaches for ensuring power availability in data centers. Here are the key differences between the two:
(1)UPS System Design: A parallel redundant UPS system involves multiple UPS modules working in parallel to provide power to the load. If one UPS module fails, the remaining modules take over, ensuring that power is still available to the load. On the other hand, a load balancing system (LBS) for UPS systems involves multiple UPS units that are connected to the same load but operate independently. In this case, the UPS units share the load based on their capacity, and if one unit fails, the load is automatically shifted to the other UPS units.
(2)Efficiency: Parallel redundant UPS systems can be less efficient than load balancing systems since they typically run all the UPS modules at partial load. In contrast, LBS systems operate each UPS unit at close to its rated capacity, which can result in higher efficiency.
(3)Scalability: Parallel redundant UPS systems are more scalable than LBS systems since additional UPS modules can be added to the system to provide additional capacity. In contrast, LBS systems typically have a fixed number of UPS units that cannot be easily expanded.
(4)Cost: Parallel redundant UPS systems are typically more expensive than LBS systems since they require more hardware components, such as additional UPS modules, cabling, and switchgear.
In summary, both parallel redundant UPS systems and load balancing systems can provide power availability in data centers. Parallel redundant UPS systems are more scalable but can be less efficient and more expensive, while load-balancing systems are more efficient but less scalable. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the data center and the available budget.