As gradual rollout for 5G begins, we start talking about it like an integral part of the digital infrastructure. With our previous blog posts on 5G, we were still at the theoretical end of the discussion, where we have talked about the increase in data generation with 5G and diversification of data centers to absorb it. We have also analyzed the infrastructural requirements of 5G.
Each time we wrapped up the discussion for 5G, our analysis was simple – 5G is the technology from the future and will change the digital realm as we know it today. It will bring remote locations into its folds and will be directly interlinked with edge computing to deliver instantaneous results. Multiple rollouts of 5G around the world make one thing clear, in the very near future; we will wonder how we ever lived without 5G.
Is 5G just faster 4G?
Speed has been the most anticipated and talked-about aspect of 5G and true to the hype the fifth-generation cellular network does deliver much higher peak speeds. But 5G it is not JUST faster 4G, it has more to offer like – higher operating frequency, near-zero latency, supporting a higher number of connected devices, etc.
Unlike the switch of previous generations, 5G is not just amping up the existing technology but changing the technology 4G is based on. 5G is based on millimeter waves, which has a much wider bandwidth than LTE 4G bandwidth. This is the reason why 5G has so much more to offer than just some enhanced features.
5G enabled by edge computing will make many technologies a reality, which will affect every industry vertical from healthcare to education, and manufacturing to banking. It will breathe life into technologies that depend on real-time communication, such as:
- Self-driving Cars/Autonomous Vehicles
- Augmented Reality
- Artificial Intelligence
- Virtual Reality and Cloud Gaming
- Advanced Robotics
- Instant Video Streaming
- Immersive Entertainment
- Remote Healthcare and Education
- Smart cities and homes
- Smart factories
With 5G users multiplying around the world, one fundamental question remains – How exactly is 5G different from 4G?
To answer just this, we decided to analyze the two generations of wireless networks by comparing figures offered by 5G and 4G. This is what the numbers revealed-
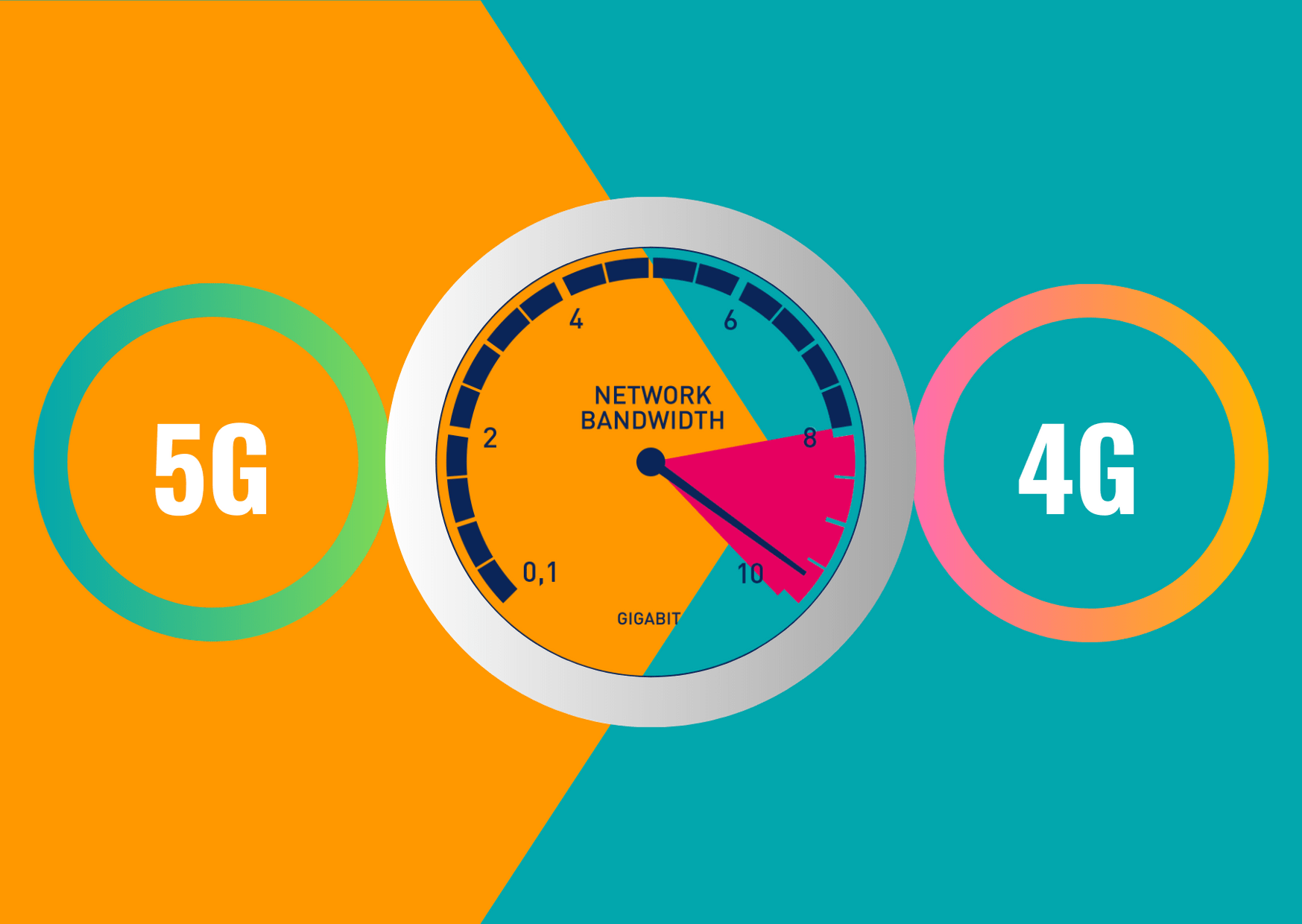
Maximum Speed Offered

Speed has definitely been a primary supporting factor for 5G from the beginning. 5G is delivering the top speed of 10 GB per second, which is approximately 6 times the current top speed of 1.45 GB per second, delivered by 4G. A Faster speed would enhance the user experience multifold and do wonders for data-intensive applications. Users will be able to stream 4K/8K videos and download multi-gigabyte files in a matter of seconds.
Reduced Latency
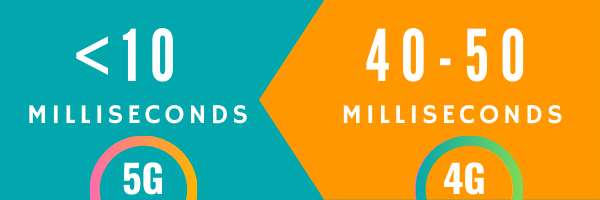
The phrase “in the blink of an eye” is about to lose its essence because 5G will transmit data multiple times in the blink of an eye. 5G is expected to function at near-zero latency, transferring data from the device, over the network to the server and back to the device in less than 10 milliseconds. This means the data will travel 4-5 times faster than 4G.
Increased Connectivity

5G will lead to a much more connected world by enabling smart cities of the future with efficient energy grids, smart transportation, and remote security. This will be possible because 5G can support up to 100 times more devices than 4G. 5G will be able to support up to 1 million devices up from a maximum of 100 thousand by 4G.
Energy Efficiency

Energy consumption is an important factor for the battery life of mobile devices and has always been a cause of concern for users of smart devices. 5G is estimated to consume almost 90% less energy per bit as compared to 4G. Zero-latency 5G networks will allow for more data to be processed at the network rather than on the device. This will mean the devices will use less energy and have longer battery lives.
Increased Data Volume

With 4G today, areas with high-density that have thousands of connected devices on the same network suffer from connectivity issues and data transfer speeds drop-down at peak hours. 5G will be able to handle 1000 times the volume of data compared to 4G, with faster speeds and lower latency.
References
https://datamakespossible.westerndigital.com/5g-vs-4g-side-by-side-comparison/
https://www.rfpage.com/what-are-the-difference-between-4g-and-5g-technology/