Communication Service Providers (CSPs) are continuously looking for new opportunities and revenue sources to enhance their businesses. As the mainstreaming of 5G begins the enterprise area looks more future-oriented and data-driven. According to a report by Ericsson titled “5G for business: a 2030 market compass”, by the year 2030 up to USD 700 billion of the 5G-enabled, business-to-business value could be addressed by CSPs.
For most CSPs, edge computing will not just ease the business processes but massively enhance their enterprise offering. Like the Internet of Things (IoT), servers based on edge computing will allow for a wider base of enterprise offerings like dedicated networks.
Why Communication Service Providers are Targeting Edge Computing?
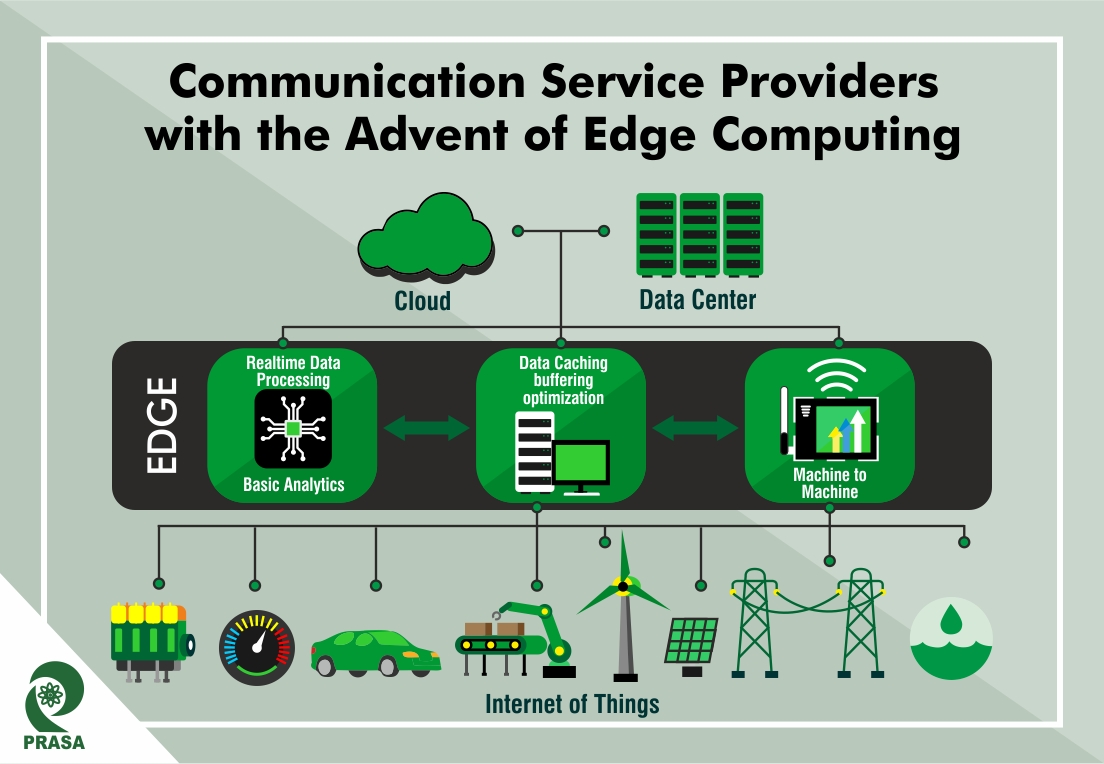
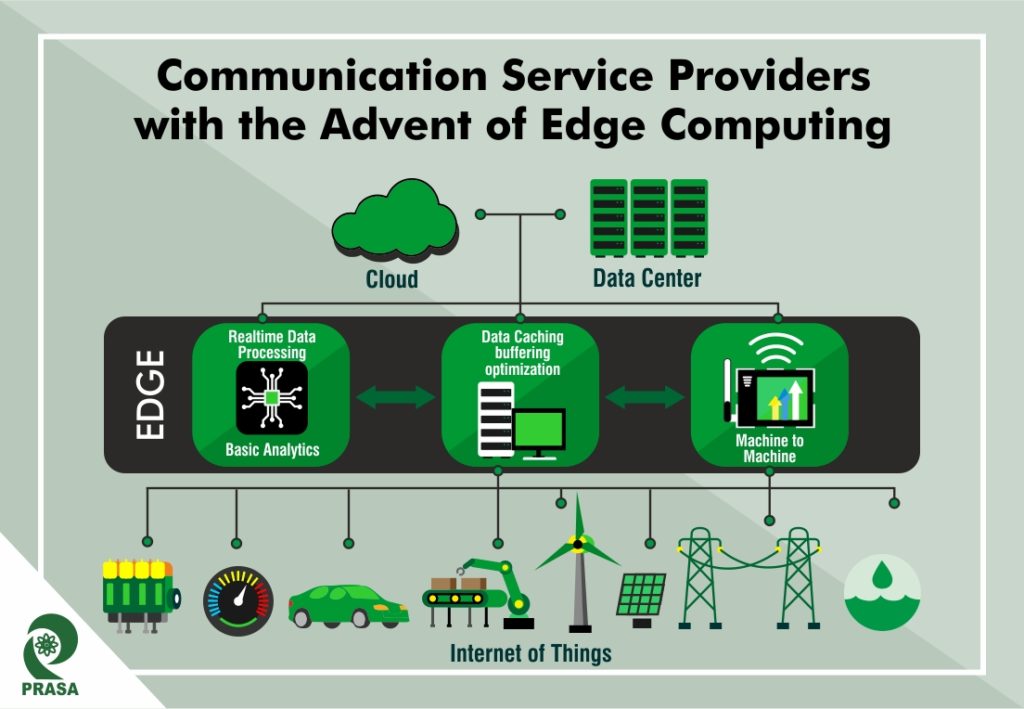
Edge computing is applicable where high-quality services and better user experience is needed to be delivered with bandwidth, low-latency, and on-location management of a huge volume of data. Edge computing works on the principle of taking the data away from the centralized cloud and bringing the data storage, processing, and handling to edge nodes, which is located near the population hubs, where most data is generated by the end-user. These edge nodes contain micro data centers, network nodes, devices, or sensors.
With edge computing, content delivery networks (read Netflix, Amazon Prime, Hotstar, etc.), video streaming, and gaming services will no longer rely on processing data from the centralized data center which takes time in proportion to the distance of the end-user from the data center, increasing the latency for data delivery. A local edge data center will allow for a near-zero latency by all users. This will not just significantly enhance the user experience but also decrease the cost involved in transmitting data.
The promising user experience offered by edge computing has piqued the interest of many CSPs, which are transforming their networks by moving towards a software-based, cloud architecture, which not only provides a push for edge computing, with assistance to make a move from today’s virtual machine (VM) model to a cloud-native, container-based edge architecture.
CSPs have also started making the move into the regional data center and local metro networks with their distributed network infrastructure with the aim to shift closer to the customer. 5G is an important factor that steers this transformation and allows CSPs to utilize new network features in different locations across their footprint. Edge computing can enable high-performance, on-demand, and cost-effective platform for 5G, which is capable of supporting a growing number of use cases and colossal data volume.
Managing the Risks and the Rewards
As good as the end result sounds, CSPs are yet to speculate their share in the edge network chain by establishing the right business model and partner(s). CSPs have to identify the right channel for new revenue needed for the edge infrastructure along with monetizing the enhanced performance, costs, and reduced latency achieved with edge computing. They will need to figure out the willingness of the user to pay for these better services and where the ownership of the primary relationship with the customer shall lie.
Before dipping their toes in the edge pool, CSPs also need to understand the creation of a balance between managing service requests from multiple providers and which locations to cover in their edge networks. A very interesting analysis creates a need to analyze the fact that while new revenue is supposed to come from edge networking, will it constitute as new net revenue or is it diluted revenue from their existing services.
These glaring questions need to be resolved before CSPs decide to take up the edge opportunity, failing which they might risk being reduced to mere connectivity providers and lose out on all the possibility of incoming revenue. Having said this, it is also paramount to balance the risks and rewards for CSPs, as over committing to the edge investment before the market is ready with demand for these services might end up hampering the current secure revenue sources from services and developments.
While the CSPs, in general, agree that they see an opportunity in the emerging edge computing market. Edge computing and its offerings have grabbed the attention of other potential players as well, including public cloud providers, over-the-top (OTT) content players, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) vendors.
This is definitely turning out to be an interesting segment with the growth in the 5G network and edge inclinations by CSPs. So, we all wait to see how the CSPs make a place for themselves in the edge universe.